Late last spring, Armenian residents in the disputed territory of Nagorno-Karabakh heard the clamors and loud noises of construction work. At night, from their sleepy village of Khramort, they could see bright lighting and hear screeching noises emanating from the nearby region of Aghdam, across the de facto border in Azerbaijan. “We can’t be sure what they were building,” said Aren Khachatryan, a boutique winemaker whose vineyards were only 500 yards from Azerbaijani military positions, “but the sound wouldn’t stop.”
As gentle breezes gave way to the hot summer months, the specter of violence for those living in the ethnically Armenian enclave increased. Azerbaijani soldiers would periodically open fire on the harvesters picking grapes for Khachatryan and his father, Arkadi, the two men told New Lines.
Soon, rumors swirled that Azerbaijani soldiers had prevented a man from leaving Nagorno-Karabakh to seek medical treatment in Armenia, promising him a bleaker future than dying untreated: He would instead be sent to a large prison complex being built for the men of the self-declared republic. In September 2023, after nine months of living under a siege that cut off access to essential goods including food and medicine, Nagorno-Karabakh was captured by Azerbaijan in a rapid military operation. Since the assault, the overwhelming majority of the region’s 100,000 people have fled for neighboring Armenia. Baku has said it seized control of territory that was rightfully part of Azerbaijan — “Azerbaijan restored its sovereignty as a result of successful anti-terrorist measures in Karabakh,” said the country’s President Ilham Aliyev in a televised address on Sept. 20, while Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan accused its neighbor of “ethnic cleansing.”
The goal Aliyev had long sought — “If they do not leave our lands of their own free will, we will chase them away like dogs,” he proclaimed in an October 2020 wartime address to his nation — was now a reality: The long Armenian presence in Nagorno-Karabakh, or Artsakh, as it is known to Armenians, had ended. On Jan. 1, the self-declared republic formally ceased to exist, a condition of the cease-fire that ended Azerbaijan’s military operation.
Using satellite imagery of both the site of a potential prison and surrounding areas, applying lessons drawn from the politics of memory and the region’s history of heritage crime, and constructing a timeline leading up to the depopulation of the region, New Lines has pieced together the role played by intimidation in the dissolution of Nagorno-Karabakh, cultivated by Azerbaijan over many months leading up to the September attack. Nagorno-Karabakh’s violent end is a chilling lesson of the risks involved in aspirant statehood, and one that feels especially relevant today.
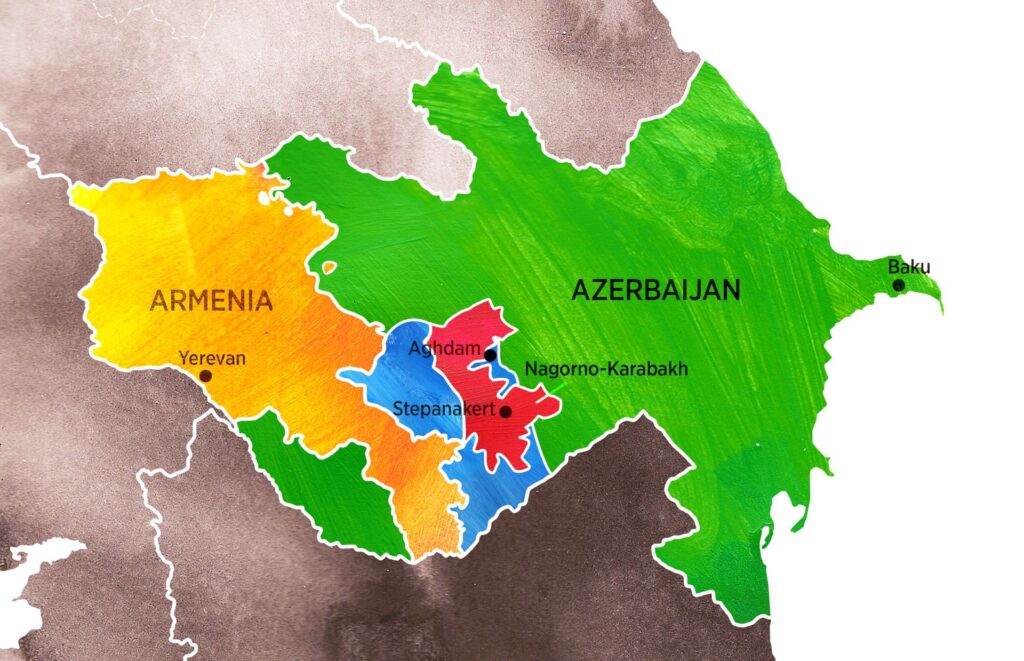
The top court of the United Nations recently acknowledged how coercion by Baku has played a role in the conflict. In mid-November, judges at the International Court of Justice ordered that Azerbaijan allow those who recently fled their homes to return to Nagorno-Karabakh “in a safe, unimpeded and expeditious manner” and “free from the use of force or intimidation” that caused them to flee.
In August of last year, Ara Papian, a former Armenian ambassador to Canada and leader of a pro-Western party, said on an Armenian talk show hosted by online media outlet Noyan Tapan that Azerbaijan was building a “concentration camp for 30,000 males.” The Armenian newspaper Hraparak reported the same a month later, citing an unnamed military source. Speaking on the condition of anonymity because they were not authorized to speak publicly, a high-ranking Armenian government official told New Lines that Yerevan possessed classified knowledge of the construction of such a structure before the September attack, saying the government believed it was intended for over 10,000 individuals.
The risk of incarceration was already high: Over the summer of 2023, four male civilians were detained by Azerbaijan in what local human rights groups have decried as arbitrary arrests and abductions. The most publicized of these cases is that of Vagif Khachatryan (no relation to the winemaker Aren), whom Baku accused of killing its civilians in the war between Armenia and Azerbaijan in the 1990s, charges he denied in a court of law. The 68-year-old was heading for Armenia for an urgent heart procedure, as noted by the members of the International Committee of the Red Cross who accompanied him, when he was arrested by Azerbaijani authorities. On Nov. 7, after a trial that involved a translator who occasionally misconstrued his statements — as shown on courtroom video released by the Azerbaijani authorities — Khachatryan was sentenced in Baku to 15 years in jail. This followed the detention, in late August, of three university students from the enclave who were charged with “violating” Azerbaijan’s national flag. They were later released.
Also currently awaiting trial are eight high-ranking officials of the breakaway government, including three previous presidents. Among them is Ruben Vardanyan, a former state minister. The Russian-Armenian philanthropist and businessman, who founded an international high school in the Armenian countryside, was detained in September while trying to cross into Armenia and is now languishing in an Azerbaijani jail.
Azerbaijan’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs did not respond to New Lines’ request to clarify the nature of the construction identified by satellite imagery.
The Nagorno-Karabakh conflict, driven in part by a century-long enmity between Christian-majority Armenians and Muslim-majority Azerbaijanis, saw its first intercommunal clashes during the Russian Revolution of 1905. The Soviet Union, to which both countries belonged, largely managed to keep ethnic tensions at bay, but these unfroze as the superpower began to crumble in the late 1980s. Deep-rooted distrust and ethnic hatred on both sides has been intensified by the four wars that have since ensued.
Buoyed by independence movements across the Soviet bloc, ethnic Armenians in Nagorno-Karabakh, which had been designated by Moscow as an autonomous region within Soviet Azerbaijan, sought unification with Soviet Armenia. The peaceful 1988 protests in the regional capital of Stepanakert were met with violence elsewhere in Soviet Azerbaijan, including anti-Armenian pogroms and expulsions, which prompted the formation of Armenian self-defense units, transforming both the nature and the scope of the conflict. Years of war and mutual bloodletting followed. By the time a Russian-brokered cease-fire was signed in 1994, at least 1 million people had been displaced, according to Human Rights Watch. In October last year, the New York-based group estimated that 700,000 ethnic Azerbaijanis were then either expelled or displaced from Armenia, Nagorno-Karabakh and seven surrounding districts, while 300,000 to 500,000 ethnic Armenians fled or were expelled from Azerbaijan.
Defeated and traumatized, Azerbaijan soon developed into an oil-producing, authoritarian and dynastic regime whose political legitimacy depended almost exclusively on its revanchist posture. Equally important was the cultivation of the image of the Armenians as the leading existential enemy of the people of Azerbaijan. Hatred has been common on both sides — some Armenian nationalists belittle Azerbaijanis by declaring that “Coca-Cola is older than Azerbaijan,” an English-language phrase that first appeared a decade ago on the online Armenian news site mamul.am. Accompanied by a photo of the drink with the year 1892 and the flag of Azerbaijan with the year 1918, the phrase became a popular social media meme during the 2020 war — a nod to the notion that Armenia is an ancient state while its enemy is an extension of Turkey and not a real country in its own right. The Azeri language is Turkic, and Armenians often refer to Azerbaijanis as “Turks,” a terminology that connects them in the Armenian psyche with the perpetrators of the Armenian Genocide of 1915. Until the early 20th century, Azerbaijanis were referred to as “Tatars,” a generic name for Turkic-speaking people.
Yet unlike in Armenia or Nagorno-Karabakh, following the 1990s war the hatred of the enemy in Azerbaijan became institutionalized, from popular culture to news. The official virtual presidential library, ebooks.az, features regime-approved titles like “Armenian Terror” and “Armenian Mythomania,” while books that acknowledge Armenian antiquity and suffering — like prominent Azerbaijani author Akram Aylisli’s novella “Stone Dreams” — are banned on the president’s orders. “It was only a matter of time before the revanchist machinery would realize its deadly potential,” Artak Beglaryan, Nagorno-Karabakh’s former human rights ombudsman, told New Lines.
A closer inspection of the timeline leading up to the September offensive shows how Azerbaijan’s international partners paved the way for what Armenia and prominent human rights activists, like the former International Criminal Court prosecutor Luis Moreno-Ocampo, say has been a concerted effort to intimidate Armenians in Nagorno-Karabakh and permanently remove them from the region.
In September 2020, at the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, Azerbaijan, with the aid of the Turkish military and Syrian rebel fighters, launched a war against Nagorno-Karabakh. Lasting 44 days, that war came to a halt when Russian President Vladimir Putin brokered a cease-fire. Azerbaijan began to nurse other plans. Restocking its depleted military arsenal and riding a new wave of popular support following its military victory, Azerbaijan’s strongman ruler Aliyev initiated a new push to solve the question of Nagorno-Karabakh once and for all. “There will be no trace of them left on those lands,” Aliyev said in an October 2020 wartime address.
In December 2022, after having secured a wide-ranging alliance with Russia that included military cooperation, Azerbaijan once again closed the Lachin Corridor, the lifeline of Nagorno-Karabakh and its only supply route to Armenia and connection with the world at large. At the time, Azerbaijan said it did this to protect the environment. Protestors blocked transportation, saying they were acting against mining operations — but the head of Ecofront, an independent Azerbaijani environmental group, described the protest as “fake.” People who called themselves “eco-activists” were sent by a state whose economy is completely dependent on oil and gas, as Azerbaijan prohibited all traffic through the Russian-patrolled corridor.

Beglaryan, now a refugee in Armenia, said that he first heard whispers about a mass prison being built in Aghdam for Armenian men well over a year ago. “Later I received some confirmation from intelligence services that the Azerbaijani authorities had such an idea and project, but I couldn’t independently verify the information.” Nagorno-Karabakh’s authorities did not publicize the information. “Firstly,” Beglaryan explained, “we couldn’t make sure of its full reality, and secondly, we didn’t want to contribute to the Azerbaijani psychological terror against our people. However, this didn’t stop rumors from spreading.”
The fear of mass imprisonment in a country devoid of a real justice system and fostering institutional anti-Armenian hatred “significantly influenced people’s behavior during and after the September genocidal aggression,” Beglaryan said, “deepening the panic and prompting the decision to flee their homeland.” During the later stages of the blockade and the early hours of Azerbaijan’s assault, he added, “Many current and former military servicemen discarded their uniforms and destroyed their documents in an attempt to eliminate any potential evidence and facts that could be used against them.”
In Stepanakert, New Lines witnessed several incidents of people setting light to military documents and medals, creating large dumpster fires on the streets. As they fled, some families discarded photos of fallen soldiers in uniform, leaving behind, burning, shredding or hiding their visual memories of the men and women who died on the battlefields. According to at least three conversations with residents, some buried uniforms in their backyards before they departed, in the hope that they would one day return.
Following the 2020 war, numerous reports emerged of Azerbaijani torture against Armenian POWs, both physical and psychological. Armenia’s human rights defender at the time, Arman Tatoyan, the official ombudsman, reported several cases of religious discrimination against illegally held Armenian POWs. Some had their baptismal pendant crosses confiscated and desecrated; in one instance, a tattoo of a cross was burned with cigarettes. One Armenian serviceman was told to convert to Islam. When he refused, “his leg was burned, and [he] was severely beaten and ridiculed. We have never recorded anything like this before,” Tatoyan wrote in his report. Mutilations and the rape of female Armenian soldiers have been documented and publicized by invading Azerbaijani forces on social media that have been reviewed by New Lines. In the fall of 2022, at least seven Armenian POWs were executed unlawfully, apparently by Azerbaijani soldiers, Human Rights Watch reported, calling it “a heinous war crime.”
The signs of an impending invasion were visible in early September, following a high-stakes meeting on Sept. 4 between Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan and Putin where they discussed key regional issues, including Ukrainian grain exports. On Sept. 7, the Armenian government expressed official concern over Azerbaijan’s military buildup around its sovereign borders, as well as around Nagorno-Karabakh. A few days prior, the investigative Armenian publication Hetq reported that there had been an increase in Azerbaijani cargo flights to the Ovda military base in southern Israel, where munitions are also stored.
In the past, as documented by the Israeli newspaper Haaretz, this had often been an indication of an impending attack. There have been Israeli arms sales worth billions of dollars over the years to Azerbaijan, the newspaper reported, including a diverse range of weaponry from sophisticated radar systems to a wide range of drones and antitank missiles.
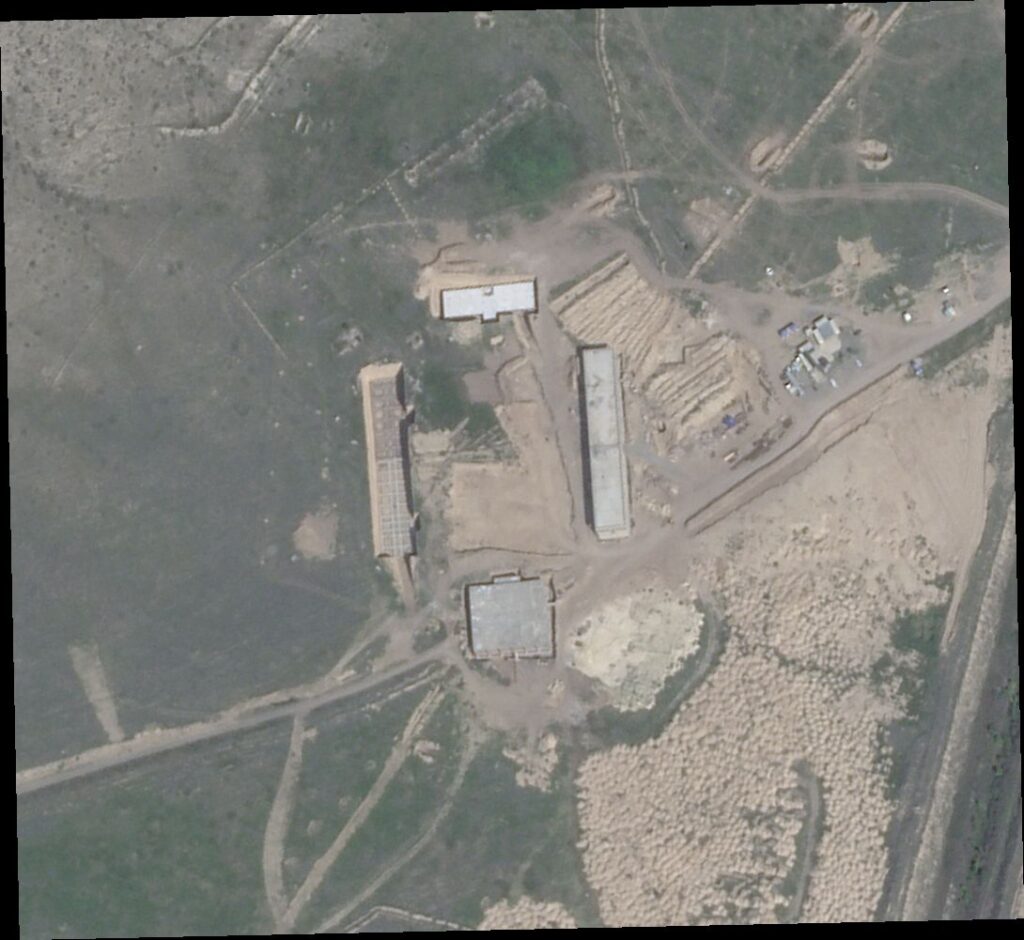
Utilizing Planet Labs satellite imagery, we have identified a site of interest that is the likely basis for the “concentration camp” fears. Nestled directly south of a key archaeological complex, near the village of Shahbulaq, there is a large, recently built but unfinished structure. To assess whether the complex was an intended prison, we applied spatial analysis methods to identify characteristics commonly associated with correctional facilities in the wider region, particularly the “medieval torture” facilities analyzed by Crude Accountability in Turkmenistan and political prisons reported by Foreign Policy in Turkey, both of which were identified in satellite imagery as well.
Pattern recognition allowed us to detect recurring elements, while feature-matching helped us compare these elements with known prison structures. Deductive reasoning enabled us to infer, from the presence of these features, the possibility that the facility in question could be an intended prison. The construction progress of the Aghdam facility, as seen in a May 2023 satellite image, reveals gridlike structures, the kind used in prison housing units or military sleeping quarters. Despite the absence of operational prison features such as guard towers and perimeter barriers, the incomplete project’s centralized layout in a desolate landscape and substantial gaps hinting at future recreational yards suggest that the secure facility is the basis for the prison rumors.
Much of the Aghdam region, where the potential prison is located, was destroyed and looted in the 1990s after it fell under Armenian control and became a de facto part of Nagorno-Karabakh. It was seized by Azerbaijan in the war of 2020; by then, Aghdam had become a ghost town.
Since late 2020, the Aghdam region has served as a site for military activities by Azerbaijani forces and retains the trenches, burn scars and military vehicle tracks of past and recent wars: In early 2021, the Cornell University-based Caucasus Heritage Watch satellite monitoring project raised the alarm over likely military installations near a seventh-century Armenian church. The complex we have identified is nearby.
A time series of satellite imagery from the European Space Agency’s Copernicus Sentinel–2A satellite revealed construction for the approximately 500,000-square-foot site likely began in July 2022. High spatial and temporal resolution satellite imagery (50 centimeters) from the Planet SkySat Constellation confirmed our initial findings.
The identified site contains features that could be associated with a mass incarceration facility: a single entry point, open-air space for inmates and uniform gridded structures. In places where government transparency is limited, such as the authoritarian regime in Azerbaijan, we acknowledge the importance of further corroborating these findings with various independent sources wherever possible.
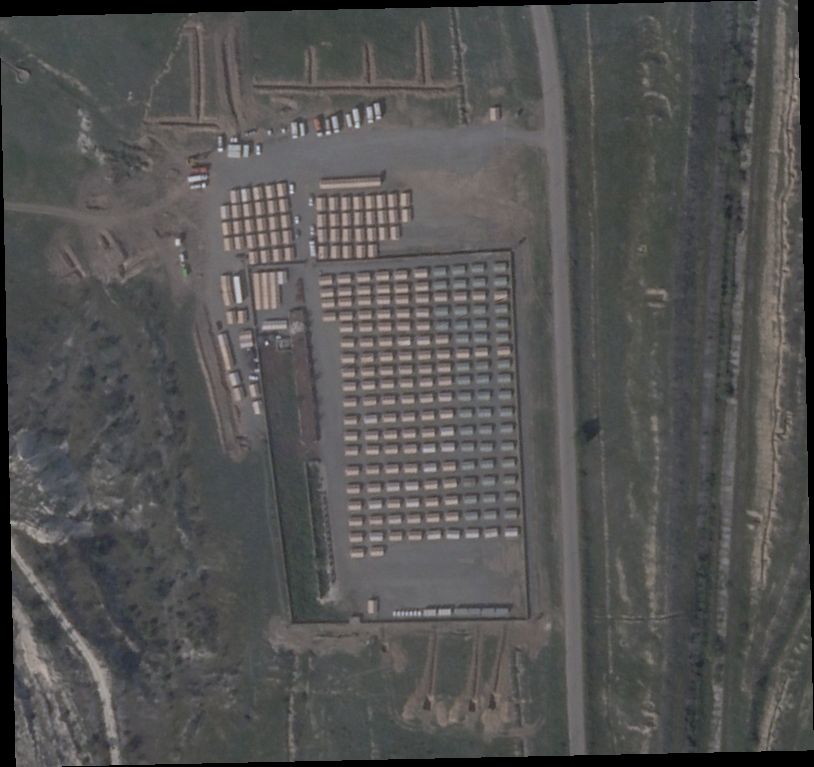
That the Aghdam facility is, at the bare minimum, a state building is corroborated by its proximity to another government structure — a temporary tent camp: In September, more than 200 oversized tents could be seen installed in an enclosed area, likely as either lodgings for the Azerbaijani military or a planned detention center for Armenians.
Satellite imagery suggests that the complex’s construction, which appears to have started in July 2022, stopped in late August or early September 2023. It was shortly before this period that Aliyev described in an interview with Euronews TV that he was seeking an end to the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict. Referring to the November 2020 cease-fire declaration between the two countries, Aliyev said, “That was a capitulation act by Armenia. Therefore, we started to put forward some initiatives in order to find the final solution to our conflicts with Armenia.”

The May 2023 announcement by the U.S. State Department that it welcomed Azerbaijan’s “consideration of amnesty” suggests specific knowledge by Washington of an incarceration plan. A spokesperson for the State Department, in emailed comments to New Lines, declined to comment on a potential prison complex, instead reiterating that Azerbaijan must “create the conditions for the voluntary, safe, dignified and sustainable return of Nagorno-Karabakh Armenians.”
The ongoing incarceration of leaders like the businessman Vardanyan, argued the former prosecutor of the International Criminal Court at a U.N. meeting in early December, is meant to prevent the displaced population of Nagorno-Karabakh from returning. “It’s not just that the entire Armenian population from Nagorno-Karabakh is now displaced. … Its state leaders are incarcerated in Azerbaijan,” Moreno-Ocampo said. “This incarceration is a message to the Armenians: If you come back to Nagorno-Karabakh, you will be starved, humiliated or killed. The captivity of these people is the culmination of genocide.”
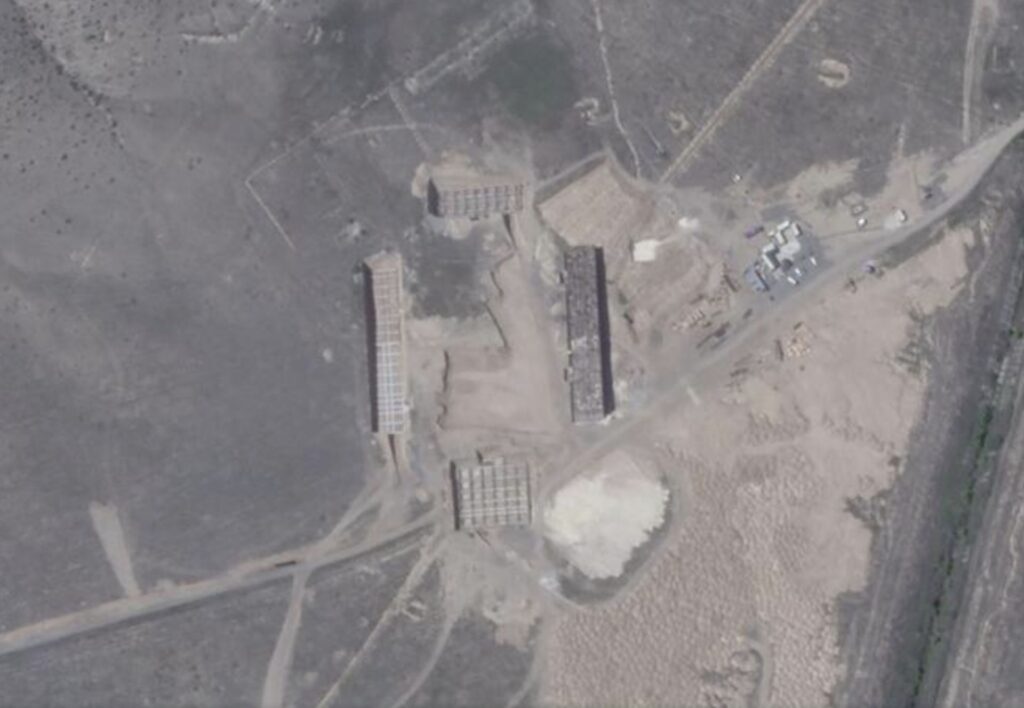

If the suspected site is indeed a prison complex, its location suggests specific psychological considerations given its proximity to important cultural monuments. The site is located on the edge of the larger archaeological complex of Tigranakert, which is home to a 2,000-year-old Hellenistic Armenian citadel, a seventh-century Armenian church and 18th-century Azerbaijani sites including the Shahbulaq fortress and a mosque. Given Azerbaijan’s denial of ancient Armenian roots in the region, which has extended to the eradication of the entire known inventory of Armenian Christian heritage in the region of Nakhichevan in 1997-2006, as well as more recent activity such as the shelling of the Tigranakert citadel in 2020 and ongoing destruction as documented by Caucasus Heritage Watch, the site selection could suggest an intention to maximize psychological trauma.
Several individuals familiar with the area whom we spoke with said the secluded site was previously home to Soviet-era barns, describing the terrain as largely unfit for development. They also noted the existence of the nearby limestone quarry, wondering if the site was primarily chosen because of the immediate availability of the key building material. A former member of Nagorno-Karabakh’s military, speaking on condition of anonymity, told us that the sounds that Armenian residents of Khramort had been hearing may have been the quarry’s nonstop stone-cutting operations. The absence of any mention of the structure is conspicuous in Azerbaijani media outlets and on the president’s website, platforms that otherwise extensively highlight every new construction project in the Aghdam region. It is also notably missing from any publicized plans. The only references on Azerbaijani websites to the Armenian fear of a massive prison, as several Azerbaijani researchers confirmed to New Lines, are stories that cite Armenian news reports.
A map produced by the “Karabakh Revival Fund,” founded by Aliyev in January 2021, ostensibly to improve living conditions in territories newly under Baku’s control, shows no development plans for the area of the identified site — except for a planned forest between it and the rest of the region — underscoring the secretive nature of the project.
Once under Azerbaijan’s control, the archaeological site of Tigranakert was declared “over,” as Hikmet Hajiyev, who serves as assistant to the office of Aliyev, posted on X (formerly Twitter). Armenian archaeologists say the site was fortified over 2,000 years ago by the country’s most powerful king — a history that Prime Minister Pashinyan instrumentalized in early 2020, telling the Munich Security Conference: “When Armenian King Tigran the Great was negotiating with Roman general Pompeius, there was no country named Azerbaijan.” If the nearby Aghdam facility is indeed the rumored “concentration camp,” its close proximity to Shahbulaq and Tigranakert is symbolic of Azerbaijani claims to domination over Armenia. Such a weaponization of heritage bears a psychological resemblance to other instances of the regime’s approach to the conflict, including what Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty has described as a theme park of ethnic hatred in the capital Baku, erected soon after the 2020 war, which publicly celebrates victory over a caricatured, hook-nosed enemy.
For the ethnic Armenians who once called Nagorno-Karabakh home, these tactics mattered, and fears of imprisonment were one of the factors spurring them toward evacuation. As Beglaryan, the region’s former ombudsman, said: The enclave’s indigenous population fled “for the sake of safety and dignity.”
This investigation was supported in part by an Armenian General Benevolent Union (AGBU) research grant.
Become a member today to receive access to all our paywalled essays and the best of New Lines delivered to your inbox through our newsletters.






